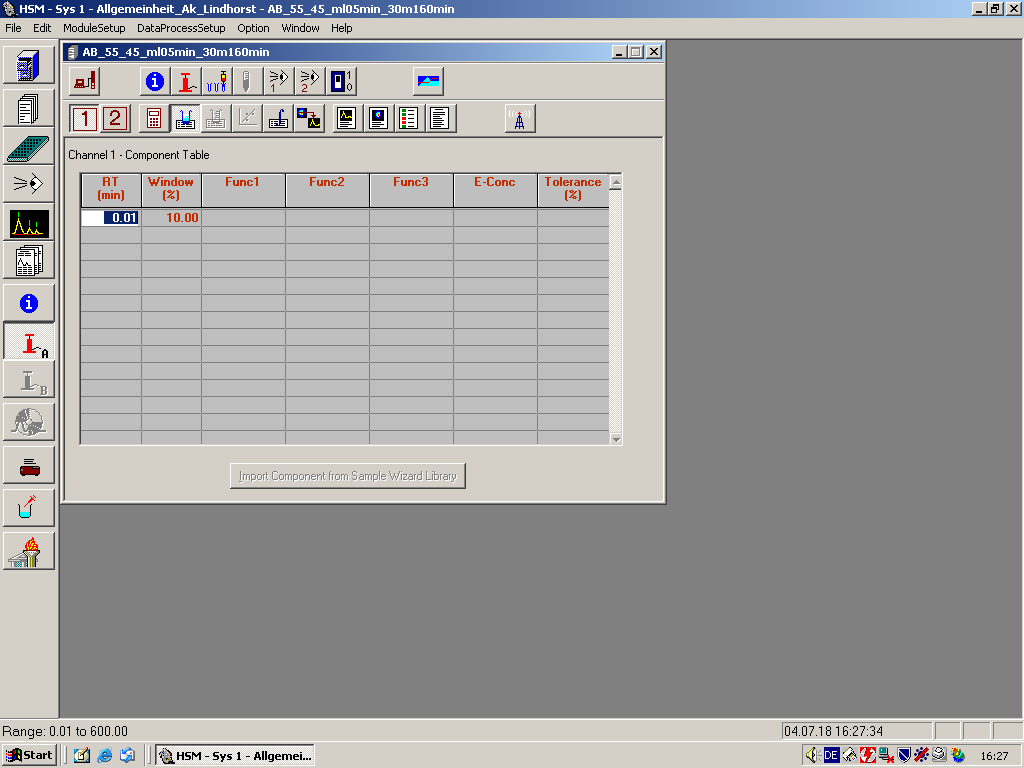
Component Table
Use this command to set up, review, or modify the Component Table for data processing. For calculation methods other than Area%/Height%, you must set up the Component Table by entering characteristics of the components that might be present in the samples. The HSM uses the information in the table to identify peaks that correspond to each component and to perform quantification and any specified functions for each component.
Note that a simple Component Table appears when Area% or Height% is selected on the Calculation Method dialog. You need to set it up only if you want to perform SST or data diagnosis on one or more peaks.
Tool Bar Shortcut
| Table Entries | |
|---|---|
| RT (min) |
Enter the expected retention time in minutes for the corresponding component. |
|
Window(%) or Window (min) The heading is determined by the selection of %Time or Absolute Time as the Peak Identification window on the Calculation Method screen. |
Enter a tolerance for the retention time.
The input value is automatically converted into a percentage time (%Time) or an Absolute Time if you change the Peak Identification window from the Calculation Method screen. |
| Name (This column is not present on the simple Component Table.) |
Enter the name of the component. The name can be up to 30 characters in length. Once the name is entered, it is automatically copied to the Concentration Table and the Coefficient Table. |
| Func1, Func2, Func3 |
Specify functions that are used for peak identification and quantitation. The functions available for this field include the following:
The REF and USE-REF functions allow you to quantify components (only for Ext-Std and Int-Std calculation method) that are listed on the Component Table and are present in unknown injections but are not included in the standard injections. They are also used to quantify peaks that are not listed in the Component Table. The REF function is used to designate a component as the reference component. The USE-REF function is used to mark components in the table that are not calibrated. The calibration coefficients of the reference component are used to calculate the concentration of any component in the Component Table that is marked with the USE-REF function. Using the USE-REF function is meaningless unless one component is designated as the reference component with REF. Also, it is not valid to mark one component as the REF as well as USE-REF component or to mark the Internal Standard (ISTD) component as the REF or USE-REF component.
Note: In the simple Component Table for Area% method, only the SST and E-CONC functions are available under Func1 and Func2.
|
| Molecular Weight This column is not present in the simple Component Table for Area% method. |
The molecular weight is used when the concentration is calculated for the desired units in the first and second concentrations. The molecular weight have a range from 0 to 999999.000. The unit conversion for the Concentration Table uses the molecular weight. However, when concentration data from the Sample Wizard is selected, molecular weight is not used in data processing. |
| Multiplier |
Specifies the multiplier for calculating Conc2 and Conc3 concentrations when the Use Component Multiplier on the Report Format screen is checked. If it isn't checked, the multiplier is not used in the calculation. |
| E-Conc |
Specifies the expected concentration of the component. This field is read-only unless the E-Conc function is selected on the same row. |
| Tolerance (%) |
Enter the tolerance as a percentage. This field is read-only unless the E-Conc function is selected on the same row. |
| Import Component from Sample Wizard Library button |
When processing chromatogram data using Sample Wizard concentration information, the component names in the Component Table should be identical to the Sample Wizard concentration information or peaks are not identified. Use the Import Component from Sample Wizard Library button to import component name and molecular weight information directly from the Sample Wizard component library to the Component Table. This button is enabled only when all of the following conditions are true:
When you click on the Import Component from Sample Wizard Library button, the Import Component Method Component Table dialog opens. Note: You can add or delete rows in the Component Table using commands in the Edit menu. When this happens, the corresponding rows in both the Concentration Table and the Coefficient Table are automatically changed accordingly. |