NiPorph • NitroPy Rotationsbarrieren: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Zur Navigation springen
Zur Suche springen
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
{{:NiPorph • Ligand Rotationsbarrieren}} | {{:NiPorph • Ligand Rotationsbarrieren}} | ||
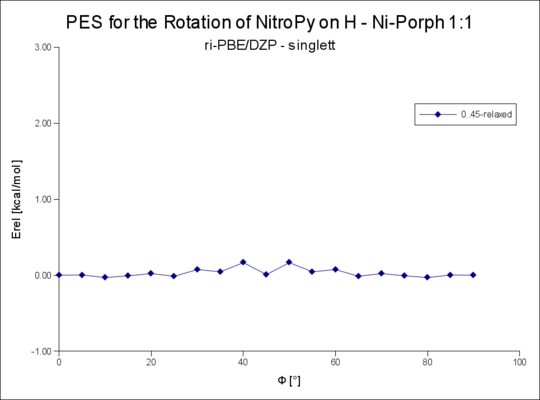
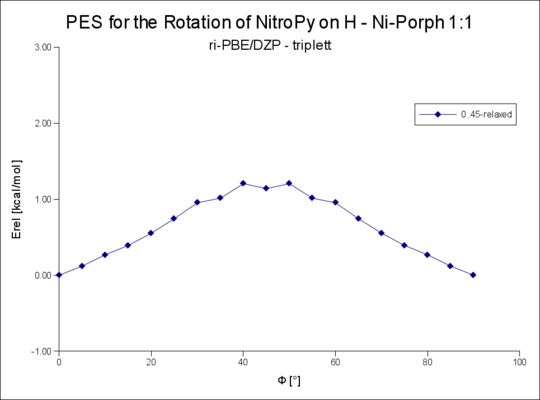
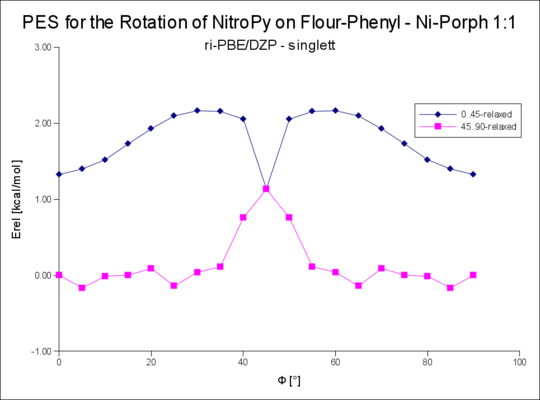
== Rotation um die R-NiPorph · | == Rotation um die R-NiPorph · NitroPy Bindung == | ||
{| {{table}} | {| {{table}} | ||
Version vom 5. Januar 2010, 14:53 Uhr
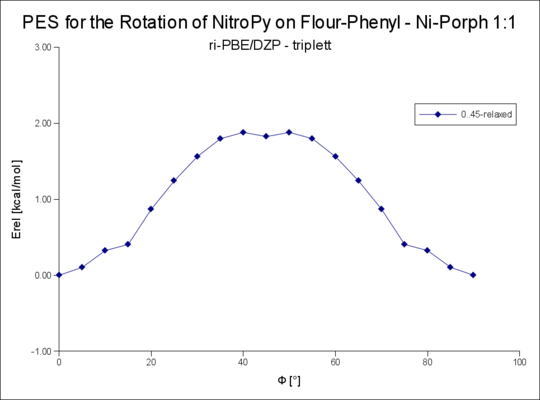
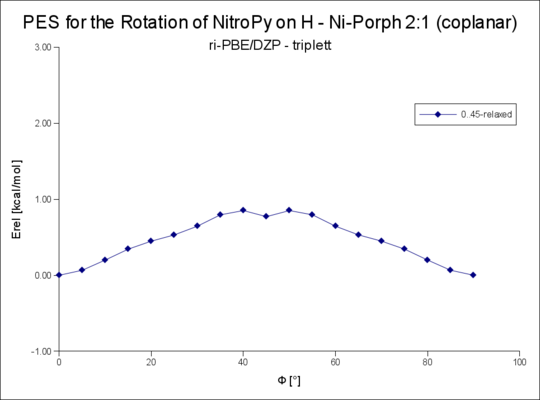
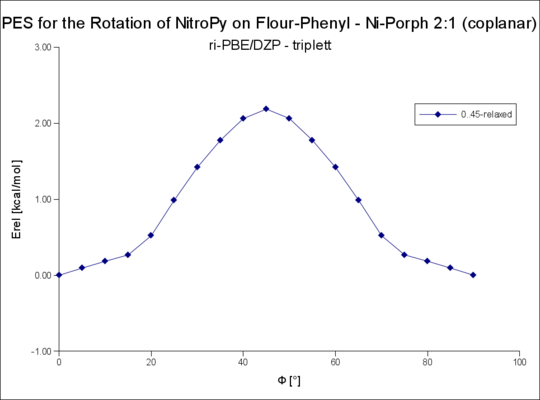
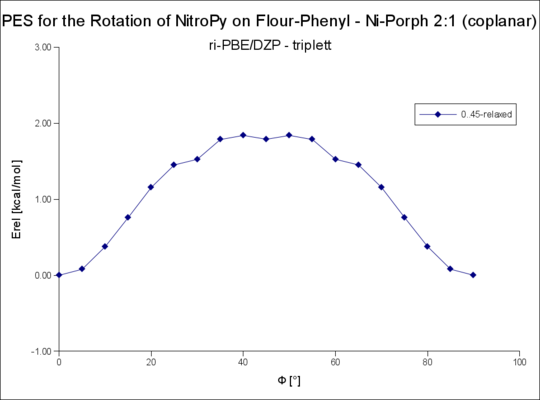
Rotation um den Winkel Phi von 0..90°
- Theoretische Untersuchungen zu Ni-Porphyrin • Ligand Komplexen
- NiPorph • Ligand Rotationsbarrieren
- NiPorph • Py Rotationsbarrieren
- NiPorph • NitroPy Rotationsbarrieren
Rotation um die R-NiPorph · NitroPy Bindung
| R=H | R=FlourPhenyl | |
| 1s | 0.20 | 1.03 |
| 1t | 1.21 | 1.88 |
| 2t(d2d) | 0.85 | - |
| 2t(coplanar-nah) | - | 1.84 |
| 2t(coplanar-fern) | - | 2.19 |
Graphen 1:1 Komplexe
- 1:1-Komplexe
Graphen 2:1 Komplexe
Die 2:1 Komplexe mit R=Flourphenyl sind asymmetrisch. Einer der Liganden ist näher ans Nickel gebunden, der andere bildet stärkere Wasserstoffbrücken mit den Flour-Atomen des Flourphenols.
Im folgenden ist die Rotationdes näher gebundenen als 2:1 (coplanar nah), die des entfernter gebundenen als 2:1 (coplanar fern) bezeichnet.
- 2:1-Komplexe
- Plot der H-NiPorph-NitroPy-Rotationsenergie PBE-DZP 2-s-coplanar.png
2:1 singlett R=H